

On April 27, 2023, Professor Wang Xinghuan's team from Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University published the latest research findings titled "DNA polymerase POLD1 promotes promotion and metathesis of blade cancer by stabilizing MYC" in Nature Communications.

In the previous study, the research team used "tumor traceability technology" to infer that POLD1 is a key molecule in the malignant transformation of bladder cancer from the perspective of molecular archaeology in a bladder cancer family. This study was published in Cell Mol Immunol in 2020[2].
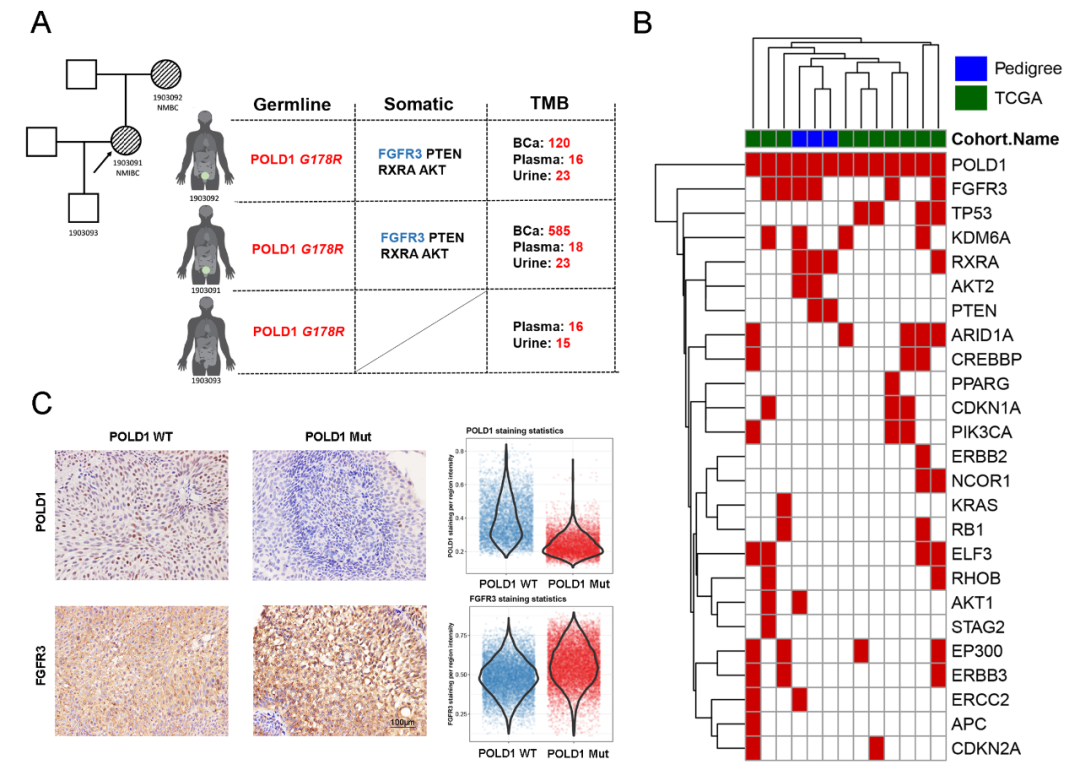
On this basis, this study confirmed that POLD1 is more highly expressed in bladder cancer than in paracancer tissue, and more highly expressed in muscularis invasive bladder cancer than in non-muscularis invasive bladder cancer, which is associated with prognosis. However, the carcinogenic mechanism of POLD1 overexpression remains unclear. Our team demonstrated in vivo and in vitro that POLD1 can promote the proliferation and metastasis of bladder cancer. Further mechanism studies showed that POLD1 stabilized MYC in a manner independent of DNA polymerase activity, that is, POLD1 weakened FBXW7-mediated MYC ubiquitination degradation by competitively binding MYC with FBXW7. In addition, the mechanism study also found that POLD1 and MYC bind to the promoter of MYC target gene in the form of complex, and enhance the transcriptional activity of MYC. On the other hand, MYC was able to transcriptionally activate POLD1, thus forming a POLD1-MYC positive feedback loop and enhancing the cancer-promoting effect on bladder cancer.
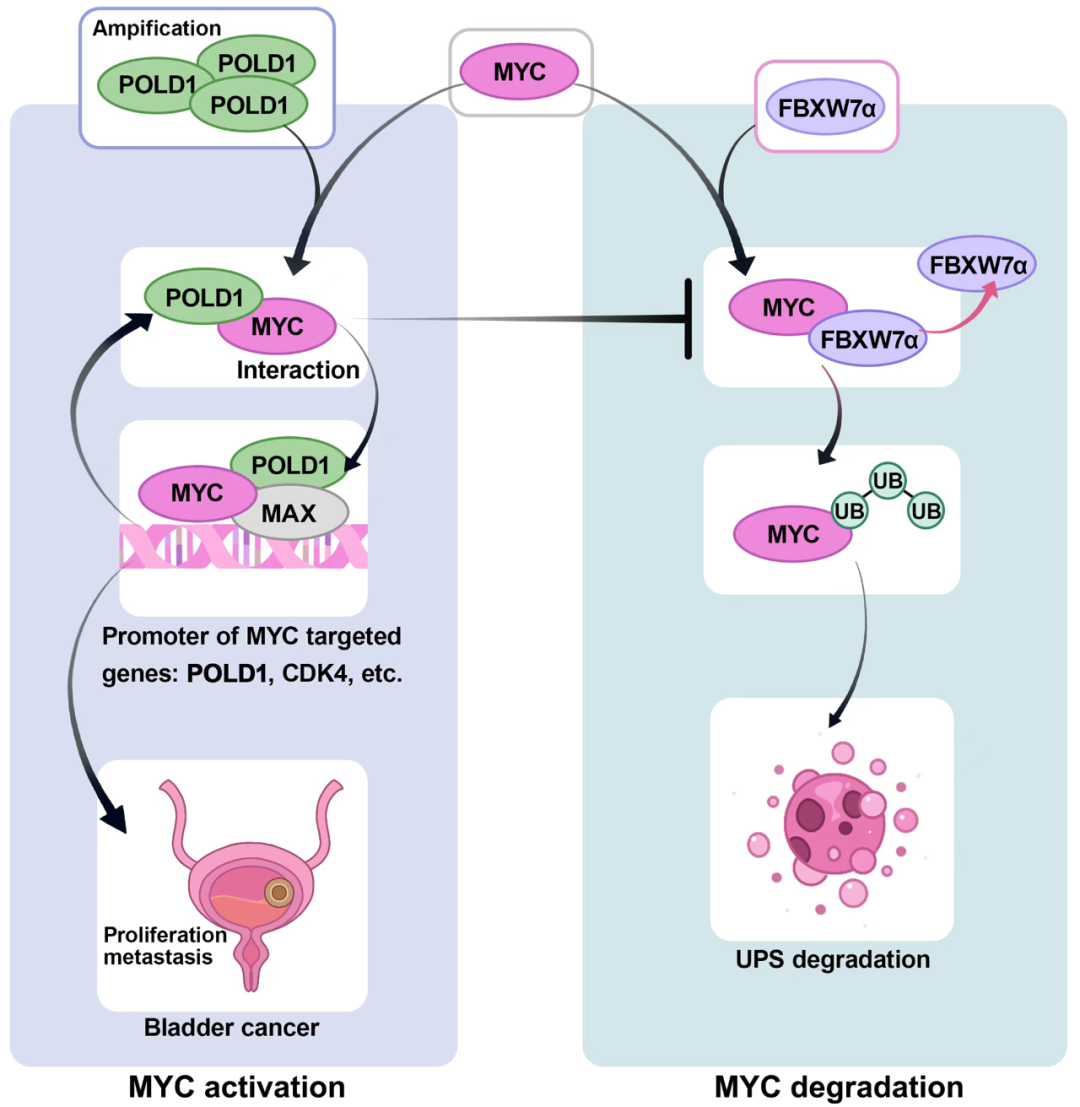
Overall, the study identifies the mechanism by which POLD1 promotes the development of bladder cancer by stabilizing MYC, and POLD1 has the potential to be a biomarker for bladder cancer. The first author of the paper is Wang Ye Jinpeng, a doctoral student in the Department of Urology at Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University. The research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Special Fund for Science and Technology Innovation of Hubei Province, and Zhongnan Hospital.
References:
[1] Wang Y, Ju L, Xiao Y, Wang X, et al. DNA polymerase POLD1 promotes proliferation and metastasis of bladder cancer by stabilizing MYC. Nat Commun, 2023; 14: 2421.
[2] Wang Y, Ju L, Xiao Y, Wang X, et al. Pedigree analysis of a POLD1 germline mutation in urothelial carcinoma shows a close association between different mutation burdens and overall survival. Cell Mol Immunol, 2021; 18: 767-9.
Links:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-023-38160-x